Metagenics MetaPure EPA/DHA Fish Oil Omega-3 200ml liquid Citrus Berry
Product Video: Metagenics MetaPure EPA/DHA Fish Oil
Directions: Metagenics MetaPure EPA/DHA Fish Oil
Take 4.2 mL daily with meals daily. Until Omega-3 Index Test is 8-12% then 1/2 dose.
MetaPure EPA/DHA Capsules may be considered to assist with the maintenance of cardiovascular health.
Clinical Benefits: Metagenics MetaPure EPA/DHA Fish Oil
- A meta-analysis of 17 randomised, controlled trials assessed the effectiveness of EPA and DHA in relieving joint pain and inflammation: The results reported a significant reduction in joint pain intensity, joint swelling, morning stiffness and the number of painful and/or tender joints at a dose of 2.7 grams per day.1 EPA and DHA exert anti-inflammatory and pain relieving actions via the following mechanisms: - Suppression of COX-2 expression and the inflammatory cytokines interleukin (IL)-1 alpha and tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha.5 - Inhibition of Leukotriene B4 (LTB4) and reduced serum C-reactive protein levels shown in in vitro and clinical trials.6,7,8
- 6 grams of EPA and DHA has been shown, in a randomised, placebo controlled study of 138 healthy males, to assist in the maintenance of triglycerides within the normal range. The study reported a significant difference in triglyceride levels by 32% in the group taking 2.6 g of EPA and DHA. The study indicated that there was a direct correlation between increased dosage and improved results.2
- A randomised, double blind, placebo controlled trial measured the mood and cognitive effects of fish oil: After 35 days, 2.4 grams of EPA and DHA was associated with an improvement in brain functions associated with attention, particularly those involving the cortical processing. There was also a significant improvement in mood states including anger, anxiety, fatigue and confusion.4
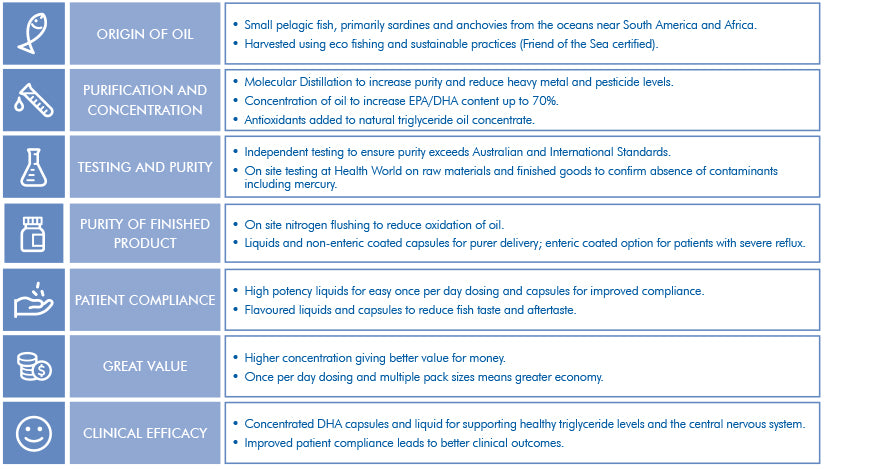
- High quality, purified fish oil: Metagenics Fish Oils are sourced from small, cold water fish using eco-fishing practices. The fish oil is molecularly distilled to ensure purity, stability and compliance with low levels of contaminants. In accordance with our leading stance on quality and purity, we have ensured that the fish oil concentrates are well below the Australian allowable levels of heavy metals, pesticides and solvents.
Ingredients: Metagenics MetaPure EPA/DHA Fish Oil
| Each 4.2mL dose contains: | |
| Concentrated Omega-3 triglycerides-fish | 4.0g |
| Equivalent Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) | 2.0g |
| Equivalent Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) | 800mg |
Metagenics MetaPure EPA/DHA Fish Oil is free from corn, dairy protein, lactose, eggs, gluten, wheat, nuts, yeast, soy protein, starches and salt. Free from artificial colours, flavours and preservatives.
Warnings: Metagenics MetaPure EPA/DHA Fish Oil
Not all cautions and contraindications are listed. For full details, references or more information contact HealthMasters in Australia by email: reception@healthmasters.com.au.
Always read the label. Use only as directed. If symptoms persist consult your healthcare professional.
Cautions and Contraindications: Metagenics MetaPure Fish Oil
Contraindications
- None of note.
Moderate Level Cautions
- Anticoagulant/antiplatelet drugs: Clinical trials have shown high-dose fish oil omega-3 fatty acid consumption to be safe, even when concurrently administered with other agents that may increase bleeding (i.e. antiplatelet or antithrombotic medications such as aspirin and warfarin). The clinical trial evidence suggests that if such an increased bleeding risk exists, the risk is very small and not of clinical significance. For example, 6.8 g of EPA/DHA daily for 6 months showed no adverse effects. However, it is reasonable to monitor patients treated with fish oils and anticoagulants for international normalised ratio (INR) as well as potential adverse bleeding experiences.83,84
- Bleeding disorders: Due to the anticoagulant properties of fish oils, there have been safety concerns in regards to the risk of increased bleeding tendency and postoperative bleeding. Although this theoretical possibility is not reflected functionally in human studies, it would still warrant caution in situations which carry a high risk of bleeding such as haemorrhagic stroke and postoperative events. To minimise the risk of exacerbation of these bleeding events it is recommended to discontinue use of fish oils during acute bleeding episodes, such as during and immediately after a haemorrhagic stroke, or in patients who are at high risk for haemorrhagic stroke.85,86
- Surgery: Due to the anticoagulant properties of fish oils, there have been safety concerns in regards to the risk of increased bleeding tendency and postoperative bleeding. Although this theoretical possibility is not reflected functionally in human studies, it would still warrant caution in situations which carry a high risk of bleeding such as haemorrhagic stroke and postoperative events. To minimise the risk of exacerbation of these bleeding events it is recommended to discontinue use of fish oils 4-7 days before elective procedures which have a high risk for bleeding complications. However, consider fish oil supplementation postoperatively if there are no bleeding complications, given that supplementation may reduce the risk of thrombotic and cardiovascular events which could occur following major surgery.87,88
References
82 Fish Oil. In: Natural Medicines Comprehensive Database [database on the Internet]. Stockton (CA): Therapeutic Research Faculty; 1995-2008 [cited 2017 Feb 21]. Available from: http://www.naturaldatabase.com. subscription required to view.
83 Bays HE. Safety considerations with omega-3 fatty acid therapy. Am J Cardiol. 2007;99(6 Suppl 1):35C-43C.
84 Harris WS. Expert opinion: omega-3 fatty acids and bleeding – cause for concern? Am J Cardiol. 2007;99(6 Suppl 1):44C-46C.
85 Bays HE. Safety considerations with omega-3 fatty acid therapy. Am J Cardiol. 2007;99(6 Suppl 1):35C-43C.
86 Harris WS. Expert opinion: omega-3 fatty acids and bleeding – cause for concern? Am J Cardiol. 2007;99(6 Suppl 1):44C-46C.
87 Bays HE. Safety considerations with omega-3 fatty acid therapy. Am J Cardiol. 2007;99(6 Suppl 1):35C-43C.
88 Harris WS. Expert opinion: omega-3 fatty acids and bleeding – cause for concern? Am J Cardiol 2007;99(6 Suppl 1):44C-46C.
89 Fish Oil. In: Natural Medicines Comprehensive Database [database on the Internet]. Stockton (CA): Therapeutic Research Faculty; 1995-2008 [cited 2017 Feb 21]. Available from: http://www.naturaldatabase.com. subscription required to view.
Low Level Cautions
- None of note.
Fish Oil Consumption Does Not Increase Bleeding Risk
by Lewis Chang, PhD
Fish oil is rich in omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA. Increased intake of EPA and DHA is beneficial for cardiovascular health, cognitive function, mental health, maternal and child health, immunity and inflammation. EPA and DHA supplements are becoming more and more popular across a wide diversity of people; from healthy individuals to vulnerable populations with impaired health.
Higher omega-3 concentrations may compete with fatty acids such as arachidonic acid for metabolizing enzymes. The interaction results in a decreased production of compounds that induce platelet aggregation and an increased production of compounds with anti-platelet properties, hence the anticoagulation benefits of omega-3. However, for patients who are under antithrombotic therapy (either with platelet aggregation inhibitors such as aspirin or anticoagulant drugs such as warfarin), the potential risk of bleeding due to the concurrent use of omega-3 fatty acids has been a concern by many clinicians, particularly surgeons.1,2
Multiple clinical studies have been conducted to investigate whether omega-3 fatty acids pose a clinically significant bleeding risk. So far, the findings have been consistent:
- A 2004 Cochrane review of 48 randomized controlled trials and 41 epidemiological analyses concludes that 0.4-7 g/day omega-3 fatty acids do not result in any change in clinical bleeding manifestations3
- A 2007 review of 19 clinical studies involving nearly 4400 surgical patients concludes that the risk for clinically significant bleeding was virtually nonexistent with the use of 1.4-21 g/day of omega-3 fatty acid supplements, even with the concurrent use of antiplatelet or antithrombotic medications4
- A 2013 systematic review of 10 randomized trials involving nearly 1000 adults 60 years or older concludes that there is no difference in total adverse event rates between daily use of placebo or 0.03-1.86 g EPA and/or DHA for 6-52 weeks5
- A 2014 review of 7 randomized controlled trials and 3 epidemiological studies concludes that omega-3 fatty acid treatment has no effect on the risk of clinically significant bleeding in either monotherapy or combination therapy settings and there is no support for discontinuing the use of omega-3 fatty acid treatment before invasive procedures6
- A 2017 systematic review based on 32 publications on healthy subjects and 20 publications on patients undergoing surgery finds that fish oil supplements reduce platelet aggregation in healthy subjects and do not increase intra- or post-operative bleedings in patients, and concludes that discontinuation of fish oils supplements prior to surgery is not recommended7
Despite the accumulating evidence demonstrating the safety of fish oil, the worry seems to persist, especially when at risk patients are involved.
Most recently, researchers from Danone Food Safety Centre (Palaiseau, France) and Nutricia Research (Utrecht, the Netherlands) evaluated the safety data from 8 clinical intervention studies involving over 600 patients, including oncology patients, HIV patients, ICU patients, and patients with Alzheimer’s disease.8 The levels of omega-3 fatty acids received by these patients (either via oral consumption or tube feeding) ranged from 1.5-10.2 g/day with a duration of 8 days to 52 weeks. The outcomes included bleeding-related adverse events, prothrombin time, and partial thromboplastin time. In the end, the researchers found no evidence of increased risk of bleeding with the use of omega-3 fatty acid products in these patients, with or without concomitant use of antithrombotic medications.
In summary, the legitimate concern of increased bleeding as a result of omega-3 fatty acid intake has not been supported by numerous randomized controlled trials and epidemiological studies involving a wide range or participants, from healthy young folks to surgical patients to very vulnerable older patients.
Why is this Clinically Relevant?
- Fish oil or EPA/DHA products are associated with a variety of benefits, from cardiovascular health to cognitive function to anti-inflammation
- The concern of increased risks of bleeding associated with these ingredients has not been validated by a large number of clinical studies and systemic reviews
- Clinicians should inform patients of the safety of omega-3 fatty acids for the vast majority of the population, and there is no scientific evidence supporting the discontinuation of omega-3 products prior to surgery
References
1. Bays HE. Safety considerations with omega-3 fatty acid therapy. Am J Cardiol. 2007;99(6A):35C-43C.
2. Braga M, Ljungqvist O, Soeters P, et al. ESPEN Guidelines on Parenteral Nutrition: surgery. Clin Nutr. 2009;28(4):378-386.
3. Hooper L, Thompson RL, Harrison RA, et al. Omega 3 fatty acids for prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004(4):CD003177.
4. Harris WS. Expert opinion: omega-3 fatty acids and bleeding-cause for concern? Am J Cardiol. 2007;99(6A):44C-46C.
5. Villani AM, Crotty M, Cleland LG, et al. Fish oil administration in older adults: is there potential for adverse events? A systematic review of the literature. BMC Geriatr. 2013;13:41.
6. Wachira JK, Larson MK, Harris WS. n-3 Fatty acids affect haemostasis but do not increase the risk of bleeding: clinical observations and mechanistic insights. Br J Nutr. 2014;111(9):1652-1662.
7. Begtrup KM, Krag AE, Hvas AM. No impact of fish oil supplements on bleeding risk: a systematic review. Dan Med J. 2017;64(5).
8. Jeansen S, Witkamp RF, Garthoff JA, van Helvoort A, Calder PC. Fish oil LCPUFAs do not affect blood coagulation parameters and bleeding manifestations: Analysis of 8 clinical studies with selected patient groups on omega-3-enriched medical nutrition. Clin Nutr. 2018;37(3):948-957.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Metagenics MetaPure Fish Oil
Pregnancy
- While there is evidence to support the use of these ingredients during pregnancy and a review did not identify concerns for use, Practitioner discretion is advised.
Breastfeeding
- Appropriate for use.89
Storage: Metagenics MetaPure EPA/DHA Fish Oil
Store below 30° C. After opening store at 2°C to 8°C. (Refrigerate. Do not freeze.)



